What are the challenges faced by the design of miniaturized card socket connectors?
- Share
- publisher
- Moarconn
- Issue Time
- Mar 4,2025
Summary
The design difficulties of miniaturized card socket connectors mainly focus on aspects such as space limitations, performance maintenance, manufacturing precision, and reliability assurance.
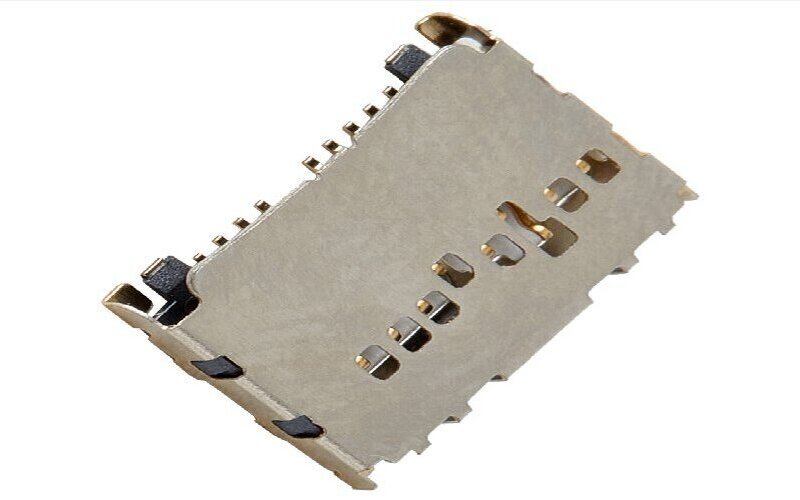
The design difficulties of miniaturized card socket connectors mainly focus on aspects such as space limitations, performance maintenance, manufacturing precision, and reliability assurance. The specific core challenges are as follows:
Balance between Material Performance and Structural Strength
- Material Selection: It is necessary to take into account both light weight and high strength (such as ultra-thin stainless steel or high-strength alloys), and at the same time ensure corrosion resistance and wear resistance (such as gold-plated contacts).
- Micro Elastic Structure: The elastic pressure plate needs to provide a stable clamping force in a very small space, and at the same time avoid fatigue failure caused by stress concentration (such as the design of a 0.1mm ultra-thin elastic arm).
High Requirements for Manufacturing Process Precision
- Development of Precision Molds: The manufacturing of molds with micron-level tolerances is very difficult, and it is necessary to control injection molding deformation (such as a micro cavity with a wall thickness of 0.05mm).
- Adaptation of Surface Mount Technology (SMT): Miniaturized pins (such as a pitch of 0.3mm) need to be compatible with high-precision reflow soldering to avoid virtual soldering or short circuits.
- Challenges in Automated Assembly: The grasping, positioning, and welding of tiny parts (such as a 0.2mm spring piece) rely on high-precision robots and visual inspection systems.
Control of Signal Integrity and Electromagnetic Interference (EMI)
- Attenuation of High-Frequency Signals: Miniaturization leads to a reduction in the cross-sectional area of the conductor, and it is necessary to optimize the structure (such as differential pair design) to reduce impedance mismatch.
- EMI Shielding Design: Achieve effective shielding within a limited space (such as grounding of the metal frame) while avoiding increasing the volume.
Thermal Management and Heat Dissipation Difficulties
- Limitation of Heat Dissipation Paths: The ultra-thin design may hinder heat diffusion, and it is necessary to select thermally conductive materials (such as metal matrix composites) or optimize the pin layout to enhance heat dissipation.
Improvement of Reliability and Environmental Adaptability
- Resistance to Vibration and Impact: The miniaturized structure is vulnerable to external forces, and it is possible to improve seismic resistance through measures such as filling with epoxy resin potting compound or designing reinforcing ribs.
- Service Life of Plugging and Unplugging: The micro contact points need to withstand more than ten thousand times of plugging and unplugging, and it is necessary to optimize surface treatment (such as a nanoscale gold layer) and contact pressure distribution.
Improvement of Compatibility and Standardization
- Interface Standardization: It is necessary to be compatible with the physical dimensions and protocols of mainstream memory cards (such as eSIM and microSD), and at the same time meet industry specifications such as JEDEC.
- Adaptability to Multiple Devices: It is necessary to be suitable for multiple devices to ensure the stability and versatility of connections when used in different devices, and reduce development costs and user usage thresholds.